Din Next Pro Condensed Font Free Download
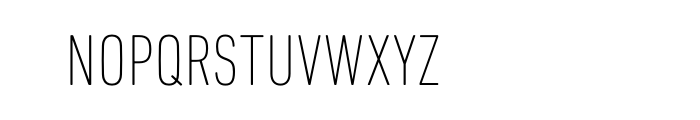

Since the introduction of the Macintosh in 1984, Apple adopted a new corporate font called Apple Garamond. It was a variation of the classic Garamond typeface, both. I Need this Font plzz DIN Next Pro Condensed Medium (http://www.myfonts.com/fonts/linotype/din-next/pro-condensed-medium/). DIN Next is a typeface family inspired by the classic industrial German engineering designs, DIN 1451 Engschrift and Mittelschrift. Akira Kobayashi began by revising these two faces-who names just mean condensed.
This article needs additional citations for. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (February 2014) (), DIN 1451 is a that is widely used for traffic, administrative and technical applications. It was defined by the standards body DIN - (German Institute for Standardization) in the standard sheet - Schriften (typefaces) in 1931. Similar standards existed for stencilled letters. Originally designed for industrial uses, the first DIN-type fonts were a simplified design that could be applied with limited technical difficulty. Due to the design's legibility and uncomplicated, unadorned design, it has become popular for general purpose use in signage and display adaptations.
Many adaptations and expansions of the original design have been released digitally. Early DIN-Fette Engschrift specimen. Fette Engschrift is a single weight of the DIN 1451 typeface. The DIN 1451 typeface family includes both a medium ( Mittelschrift) and a condensed ( Engschrift) version; an older extended version ( Breitschrift) is no longer used since the early 1980s, but may still be encountered on older road signs in Germany. DIN 1451 is the typeface used on road signage in Germany and a number of other countries.
It was also used on from 1956, until replaced there in January 1995 by, a typeface especially designed to make the plates more tamper-proof and to optimize automatic character recognition. The typeface has gained popularity due to its wide exposure through its release as a typeface in 1990. Since then it is also used by non-governmental organisations and businesses. For graphic design and desktop publishing, several offer redesigned and extended versions of this typeface. The design included not only the DIN 'Engschrift' but also a DIN 'Mittelschrift' (medium width, now very popular. A DIN 'Breitschrift' (Extended) design was also included, but it has never been widely used. In order to enable quick and easy reproduction, all drawings were originally based on a coarse grid and could be executed with compass and rulers.
The standard sheet DIN 1451- Schriften (typefaces) was released in 1931 as a pre-norm. With some minor changes DIN 1451 was officially released as a norm in 1936. In 1938 Temporary Order No. 20 required DIN 1451 to be used on the new German (motorways).
This and other similar regulations resulted in DIN 1451 dominating German public lettering until today. Stencils for lettering technical drawings to DIN standards Within the scope of public and the use of the DIN 1451 typefaces spread rapidly, once they were adopted. They were released as lettering stencils for smaller applications, as larger metal stencils for application to machinery, vehicles and airplanes, and as cast metal lettering for street and building signage.
Printing types according to DIN 1451 have never been produced though. During DIN 1451 was also adopted for the.
The 1943 version of DIN 1451 also included a showing of characters, although their design did not match the weight and proportions of DIN Mittelschrift. Keygen Draw Plus X6 Reviews. Geometric sans serif lettering and typefaces were very popular in the 1920s and 1930s.
At the the design of lettering on coarse grids was advocated by and during the Dessau period. Although being designed in a similar way, the DIN typefaces lacked elegance and did not take advantage from these design trends. Inspired by the DIN standard, a consortium of Dutch organisations created an equivalent standard lettering, NEN 3225. Created by a group of designers including, the design has no similarity to the DIN standard: it is a humanist family with serif and sans-serif styles. The sans-serif is similar to and and the serif on the Garalde model. Releases [ ].
A sign in an older version of DIN Mittelschrift. Note the different structure of the 'a' and how curved strokes do not thin as they connect, as at the join of the 'h'. The transferable-lettering-sheet company, made several variants available in the 1970s. Also the type foundry adopted the DIN typefaces for their optomechanical systems such as Staromat. In 1980 the DIN typefaces were redrawn by Adolf Gropp (1911–1996), a lettering artist from. The drawings were made on a finer grid. This enabled an exact definition of details such as the amount of overshoot of round characters (e.g.